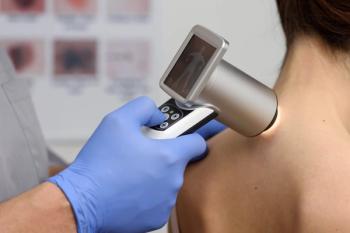
Dermatoscopy identifies visual features that predict melanoma metastasis risk, performing comparably to current pathology-based staging methods.

Dermatoscopy identifies visual features that predict melanoma metastasis risk, performing comparably to current pathology-based staging methods.

Flipped dosing of Yervoy and Opdivo produced a 49% response rate compared with 37% for the standard dose of the combination and extended survival to 42 months from 14 months in a Swedish study.

The Melanoma Research Alliance launched a national biorepository at the University of Colorado to collect melanoma samples, focusing on rare subtypes for diagnostic and treatment research.

The patch measures distinct electrical patterns, which indicates how easily electrical signals pass through living tissue. Cancerous areas have different electrical properties than healthy skin.
A phase 1 trial highlights the role the microbiome plays in resistance to checkpoint inhibitors, as well as to immune-related adverse events from treatment.

UCLA study reveals why melanoma returns after immunotherapy: tumors delete genes triggering cell death while copying survival genes. This understanding could potentially enable new combination treatments to prevent resistance.
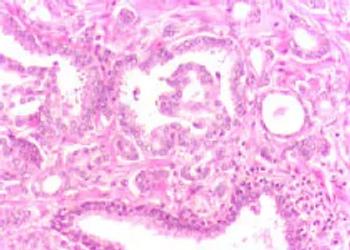
An NYU-led study found Keytruda immunotherapy after surgery lowered the risk of Merkel cell carcinoma spreading to the liver, lungs and bones.
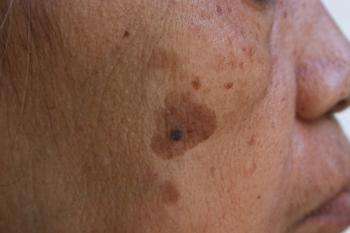
In a viewpoint column, some experts are suggesting that melanoma in situ, which generally doesn’t lead to invasive melanoma, as a precancer to reduce unnecessary biopsies, surgeries, and emotional distress among patients.
Libtayo gained FDA approval as the first immunotherapy for high-risk cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, promising improved outcomes post-surgery and radiation.
An engineered CD40 antibody that can bind to a specific immune receptor and directly injected into tumors has demonstrated in a phase 1 trial that it can trigger a systemic immune response.

Research shows older adults had 4.45 million skin cancer cases in 2021. Basal cell carcinoma is expected to double by 2050 worldwide.

In a large retrospective study of veterans, the B3 derivative nicotinamide was found to be effective at reducing the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.

Gen Z is most at risk for skin cancer due to a lack of knowledge about the sun and how to protect themselves.
A dissolvable microneedle patch delivering doxorubicin shows encouraging efficacy in a phase 2 trial to treat patients with basal cell carcinoma.

Researchers from the University of Michigan have developed a skin patch that was able to accurately detect melanoma in tissue samples from mice.
A recent study reveals that 89% of patients with unresectable desmoplastic melanoma respond to Keytruda.
IO Biotech plans to meet with the FDA this fall to discuss the data from the phase 3 trial of Cylembio and determine next steps for a potential biologics license application submission.

The combination of RPI, a genetically engineered herpes simplex virus type 1, and Opdivo shrank both injected and non-injected tumors by 30%.
The response rate to Amtagvi was higher in patients who had received two or fewer therapies than in those with more heavily treated disease.

Studies show in mice show that targeting the metabolic pathways could inhibit the growth of melanoma and combining this strategy with other treatments could enhance the therapeutic effect.


EGFR inhibitors such as Erbitux and Gilotrif show potential in laboratory and mouse studies in treating melanoma with a specific mutation that can lead to resistance to immunotherapy.

AI apps that can detect skin cancer can be manipulated and potentially miss cases of melanoma, a serious skin cancer.

Several oral abstracts presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology’s annual meeting highlight ongoing research of Keytruda, Opdivo, Tecentriq and more in skin cancer.
Researchers are also investigating the PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor as treatment before surgical and radiation treatment.