
In high-deductible plans, patients had the highest out-of-pockets costs and abandoned and discontinued therapy at greater rates than other benefit designs.

In high-deductible plans, patients had the highest out-of-pockets costs and abandoned and discontinued therapy at greater rates than other benefit designs.

The bill would allow the Federal Trade Commission to impose penalties on PBMs of up to $1 million for unfair and deceptive practices.

Molly Beinfeld, senior research lead, evidence synthesis at the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, talks about the organization’s research assessing payer coverage policies of prescription drugs.

Doug Nemecek, M.D., chief medical officer, behavioral health at Evernorth, talks about the mental health issues teenagers are facing.

Launched last year, Prime’s MedDrive is an integrated drug management solution that leverages biosimilars to help reduce drug spend.
If insulin copays were capped at $35, Part D enrollees would save 29% on average, according to new analysis from Kaiser Family Foundation.

Generics are now available for the two drugs: Vimpat and Combigan.

Aetna has made available four specialty drugs that were approved early in 2022 through prior authorization. These include a biosimilar, a CAR-T immunotherapy, and therapies for macular degeneration and a rare auto-immune disease.

The role of health economic and real-world evidence has become, and will continue to be, an important aspect of healthcare decision-making.

Financial hardship was more likely to be reported by older patients who don’t have insurance, take multiple medications, and have a low annual household income.
Drug rebates can reduce plans’ net costs but they do not reduce patients’ cost sharing.

Tracy Spencer, senior vice president at PSG, discusses what large, self-insured employers and plan sponsors want from their specialty drug benefit.

Centene is divesting both Magellan Rx and PANTHERx Rare and will exit the pharmacy benefit management space.

UnitedHealthcare considers Aduhelm unproven and not medically necessary for treating Alzheimer’s disease.
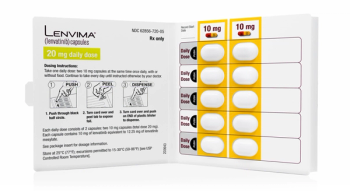
Lenvima is approved to treat thyroid cancer, renal cell carcinoma and in combination with Keytruda for metastatic kidney cancer.

Javier Gonzalez, Pharm.D., Abarca’s chief growth and commercial officer, talks about Assura, the PBM’s net cost pricing solution, which provides more predictability to drug costs and guarantees an annual fixed cost.

Pramod John, CEO, and Bhargav Raman, M.D., director, clinical product, at Vivio Health, discuss how their system can match patients to therapies based on data.

An estimated additional 81 million prescriptions were abandoned at the pharmacy because of high out-of-pocket costs for patients.

Carole Florman, policy fellow at CancerCare, talks about how utilization management can have unintended consequences for patients.

A Parkinson’s therapy, a treatment for seizures, a drug used in the treatment of heart failure, and a therapy for a rare disease have been removed from Prime’s Medicare formularies.

Capital Rx uses the NADAC model, which was developed by CMS for Medicare and Medicaid drug pricing.

Increased use of biosimilars could reduce Medicare Part D spending by 18% and beneficiaries’ out-of-pocket costs by 12%.

A literature review found an association between increased cost-sharing and lower patient adherence, which in turn could be associated with increased hospitalizations.
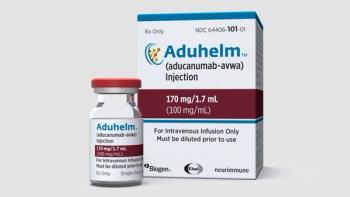
CMS’s final decision is that monoclonal antibodies to treat Alzheimer’s disease may only be covered in a randomized controlled trial conducted under an investigational new drug application.

Drew Mihalyo of Delta Care Rx discusses the company’s pass-through pharmacy pricing model.