A recent study found 64% of patients with psoriatic arthritis who had tried at least one biologic stayed with Cosentyx for the entire study period.

A recent study found 64% of patients with psoriatic arthritis who had tried at least one biologic stayed with Cosentyx for the entire study period.
Preliminary findings by Case Western researchers point to kallikrein-related peptidase 6 as possible culprit in the development of psoriatic arthritis.

Potential agents to battle inflammation and other processes move through development pipeline.

A look at recent developments in treatment and the cost implications of various autoimmune diseases.

The food people eat and the toxins they are exposed to on a daily basis are two of the biggest contributors to the likelihood of developing an autoimmune disease, according to many health experts.
Protein produced by common gut bacteria may trigger the onset of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ulcerative colitis.

Although it’s still unknown what the mechanisms are that contribute to MS-related fatigue, certain dietary approaches can help treat it.

A Yale University study has revealing findings about how diet impacts patients with lupus.

A new Chinese study highlights a potential cell therapy strategy for autoimmune diseases in a clinic setting.
A new study theorizes organs affected by autoimmune disease suppress immune cells using methods similar to those used by cancer cells to evade detection.

Results of 20-year cohort study reveal that women with history of this serious medical illness are more vulnerable to lupus.

New research has revealed that this approach could aid in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, as well as help with diabetes, chronic pain and numerous other conditions.

A new Swedish study examined gender differences in rheumatism and other autoimmune diseases. Here are the surprising findings.

A new study has surprising findings about traumatic or stressful life events and the link to developing an autoimmune disease.

A South Korean study may contribute to the improvement of personalized therapeutic outcomes for rheumatoid arthritis by expanding the scope of molecular imaging.

A new study on the overlap between the causes of rheumatoid arthritis and Huntington’s disease opens up new therapeutic targets and drugs for both conditions.

A neurologist and autoimmune expert at UT Southwestern shares insight into using large biobanks to understand and treat this rare autoimmune disease.
A Canadian study considers whether concerns over a link between the HPV vaccine and autoimmune disorders have merit.

A Canadian study has exciting findings about offspring exposed to tumor necrosis factors.
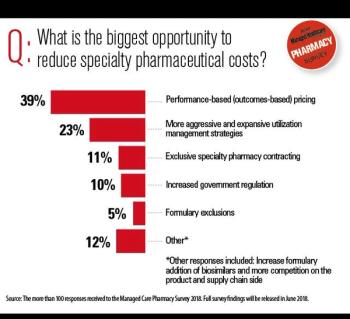
Experts weigh in on the spending outlook for these high-cost conditions.

More targeted therapies for autoimmune diseases are on the horizon. Here’s what to anticipate in 2018.

For the fourth consecutive year, diabetes therapy topped the list of contributors to drug use trends in therapeutic categories, contributing 16.1% to overall growth in drug spending in 2010 due to an increasing number of patients, according to the recently released 2011 Medco Drug Trend Report, which tracks utilization and spending.

Patients with inflammatory rheumatic disease may need 2 doses of adjuvanted split influenza A vaccine to elicit the same antibody response as healthy individuals, reported a recent Swiss study published in Arthritis & Rheumatism.

An analysis of data from more than 90,000 Medicare managed care enrollees who received care for rheumatoid arthritis found that more than one-third did not receive the recommended treatment with a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug, and that receipt varied by demographic factors, socioeconomic status, geographic location, and health plan, according to a study in JAMA.