
Time can be especially precious for people with advanced cancer. Researchers and clinicians are beginning to consider “time toxicity” as another aspect of treatment that burdens patients and their loved ones.

Time can be especially precious for people with advanced cancer. Researchers and clinicians are beginning to consider “time toxicity” as another aspect of treatment that burdens patients and their loved ones.

Researchers from the University of Utah in Salt Lake City have developed a more comprehensive, multifaceted digital tool for lung cancer screening that integrates into EHR as well as patient portals. Their paper was published in JAMA Network Open in June 2024.
In most healthy adults, RSV is mild or asymptomatic, but it can cause severe illness or hospitalization in babies, young children, older adults and pregnant women, in particular, with potential complications including pneumonia, sepsis and preeclampsia.
A recent study of children with RSV conducted by St. Jude faculty member M. Asunción Mejías, M.D., Ph.D., and colleagues emphasizes that the risk of RSV extends past infancy. The study also highlights age-specific factors associated with severe disease.

A new study in JAMA Network Open suggests that disparities in outcomes between Black and White children with acute myeloid leukemia may be due to differences in pharmacogenomics, which is how genes affect drug responses.

The study found that the average annual costs for individuals with Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) were significantly higher compared to a matched non-CLL cohort.
First approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2014, Opdivo has multiple indications across various types of cancer, including NSCLC, melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, and urothelial carcinoma.
According to a recent study in JAMA Network Open, robotic-assisted lung surgeries take a bit longer but seem to be just as safe as video-assisted surgeries.

Cancer patients not only experience the physical and mental toll of treatments like chemotherapy but also face "financial toxicity" due to high out-of-pocket costs, which can challenge their ability to work.

Crenolanib may have advantages over other therapies targeting acute myeloid leukemia with FLT3 gene mutations.
Darzalex (daratumumab) is a monoclonal antibody drug currently approved for both refractory and new multiple myeloma. It’s available in intravenous and subcutaneous formulations.

This decision may lead to faster approval of new treatments for multiple myeloma.

A group of researchers recently aimed to investigate the prognosis of patients with NSCLC that lacked a spouse, family members, or friends to support them during cancer treatment.

The term "time toxicity" has been coined for the large amounts of time taken up healthcare that may interfere with other priorities.
A recent study published in NEJM Evidence suggests that minority patients may not have equal access to CAR T-cell therapies, despite the potential life-saving benefits they offer.
Enhertu demonstrated antitumor activity against HER2-overexpressing metastatic NSCLC in the trial.


Last week, BMS announced that the FDA Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) has voted in favor of BMS’s and 2seventy bio's Abecma (idecabtagene vicleucel) for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma in earlier lines of therapy.
The trial evaluated Adcetris in combination with Revlimid and Rituxan compared to Revlimid and Rituxan plus placebo in adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL who have received two or more prior lines of therapy and are ineligible for stem cell transplant or CAR-T therapy.
Small cell lung cancer is a less common form of lung cancer and very aggressive. Researchers and drug developers are looking for new treatments, especially for patients whose cancers have stopped responding to first- and second-line treatments. Tarlatamab, a bispecific T-cell engager, looks promising as a third-line treatment.


In the U.S., nearly 200,000 new cases of lung cancer were reported in 2020, with over 100,000 deaths. While the number of lung cancer deaths has generally decreased over the past 20 years, lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer deaths in the US and is the third most common type of cancer.
Mutations in the FLT3 gene are common in AML, occurring in around 30% of cases, and tend to be associated with poorer outcomes.
A study found that the mRNA-1647 vaccine candidate developed by Moderna elicited strong immune responses. The mRNA vaccine is now in phase 3 clinical trials to determine its effectiveness in protecting against CMV.
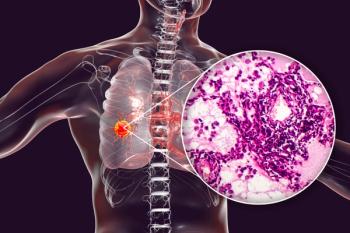
Initial treatments for lung adenocarcinomas may be effective at first, but sometimes these tumors can respond by turning into small cell lung cancer (SCLC), a more aggressive and difficult-to-treat disease.

Imbruvica is an oral medication prescribed to treat certain B-cell malignancies, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) and Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia.

The development of new and improved therapeutic agents has improved the treatment outcomes for MM over the past few decades. It remains unclear whether these racial disparities have persisted in the era of novel agents.