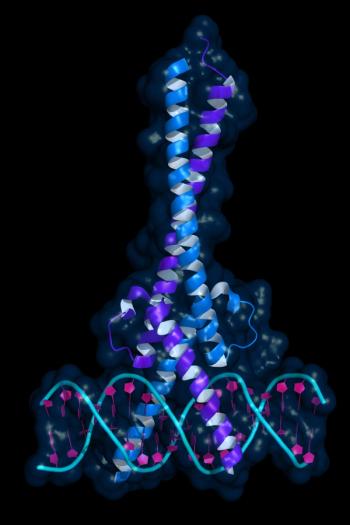
Mayo Clinic researchers find that stem cells with the highest Myc expression become dominant in driving lung remodeling .
Keith Loria is a contributing writer to Medical Economics.

Mayo Clinic researchers find that stem cells with the highest Myc expression become dominant in driving lung remodeling .

The 68-year-old Florida man is walking 106 miles from Key Largo to Key West.

Conventional drug development typically zeroes in on individual proteins or signaling pathways. By focusing on the transcription factor FOXO3, Refoxy hopes to harness a key regulator that impacts numerous biological processes.

Diagnostic criteria for pulmonary fibrosis and other fibrotic diseases in children are lacking. That void hampers an understanding of how disease progresses in children and adolescents and what the outcomes are.

The researchers hope their discoveries will lead to novel strategies to not just slow fibrosis but promote functional repair of the injured lung.
Two industry-sponsored studies investiaged needs of people with pulmonary hypertesion and interstitial lung disease.

Mouse models of liver, kidney and lung fibrosis showed that genetic deletion of MERTK prevented fibrosis
Identifying the underlying causes of prolonged lung inflammation associated with radiographic abnormalities could be key understanding long COVID and other lung conditions, researchers say.

A benzodiazepine analog produced positive results in a mouse study.

The researchers identified 32 proteins associated with rapid declines in lung function.

The company recently announced promising results from its phase 2a clinical of an agent that the company says is the first to target Traf2- and NCK-interacting kinase, or TNIK for short.

Black patients are less likely than White patients to get the molecular testing that can led to immunotherapy and other more advanced treatments.
Libtayo monotherapy nearly doubled the median overall survival and lowered the risks of death and disease progression.

“Immunity debt” may be the explanation

The data revealed that 17.1% of patients experienced grade 3 or greater arrhythmias.

Researchers that clinical guidelines highlight the possibility of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and other conditions masking early symptoms of lung cancer.
A nomogram based on four pulmonary factors is helpful but not a substitute for clinical judgment, say the authors.
Pulmonary complications remain a major cause of morbidity and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease, despite increasing research interest in the condition.
A new study conducted by researchers at the United Therapeutics Corporation in Durham, NC, looked to characterize PH-ILD disease burden by analyzing healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) and cost data.

USC researchers found a link between childhood exposure to nitrogen dioxide well below EPA limits and bronchitis symptoms in adults.

New research published in Nature Scientific Reports revealed that people with MS are more prone to experience a short-term reduction in disability and brain lesion volume after receiving stem cell therapy.

A new study out of Germany, published in Science Translational Medicine in June, looked at peripheral blood mononuclear cells and serum collected from two independent cohorts of patients with MS to identify three endophenotypes of the disease.
Researchers of a JAMA Network study observed that RSV patients seemed to be older than usual and globally sicker than usual requiring advanced respiratory support and intensive care.

From the cohort study, 67 participants developed Multiple Sclerosis after enrollment.

Up until recently, no single study had validated the relationship between lung volume and tissue and static respiratory system compliance at the applied positive end-expiratory pressure.

A new study looked to show how frequent non-coding FOXF1 gene deletions that interfere with important DNA regulatory regions can lead to a rare, lethal, genetic lung disease which causes respiratory failure in many newborns and infants.
While plenty of studies have been done looking at how blood cells function within bone marrow, new research looks deeper at other cells, and resulted in the collaborators creating a Bone Marrow Atlas.